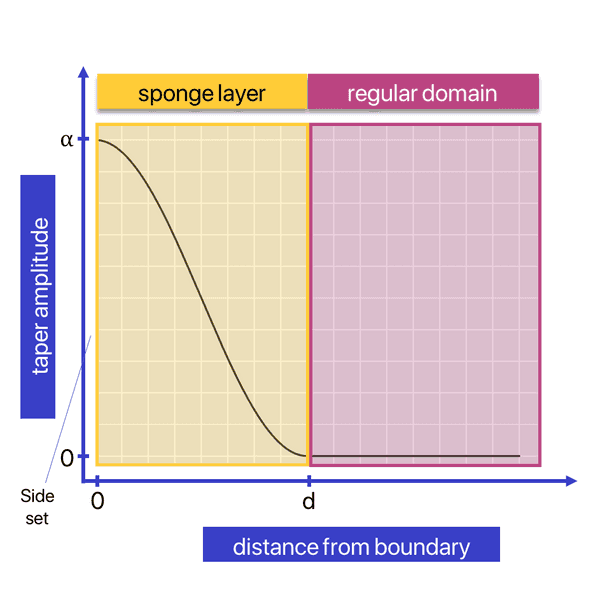
Empirical tests have shown that setting the taper amplitude equal to the dominant frequency (in Hz), and using a layer width of 3-7 wavelengths (depending on how close the sources and receivers are to the absorbing boundary) work usually well.
Absorbing Boundaries
In many situations the computational domain needs to be truncated, which requires absorbing boundaries to avoid artificial reflections.
First-order boundary condition
Acoustic media
In acoustic we apply the Sommmerfeld radiation condition:
where we assumed either a pressure or displacement potential formulation for , see here for a general parameterization of the acoustic wave equation.
Elastic media
The generalization of this condition to elastic medium is usually called the Clayton-Engquist condition, which relates the normal traction on the boundary to the normal and tangential components of the velocity field.
where denotes the normal component of the velocity field and the tangential component(s) of the velocity, respectively.
Note that in both media, the terms appearing on the left-hand-side are the same as for the natural boundary conditions, and thus vanish in the weak form.
Sponge layers
The boundary conditions above both work fairly well for waves with normal incident angle, but they are imperfect, in general, and will still allow for small reflections. Because these artificial reflections can have similar magnitudes as reflections from heterogeneities of the medium, an improved version of absorbing boundaries of often necessary.
Following the work by Kosloff & Kosloff, Salvus can introduce additional sponge layers close to the boundaries in which the wavefield is tapered.
where the taper is defined as a function of distance from the boundary as follows
The sponge layer is parameterized by two parameters, the amplitude at the boundary and the width of the layer in meters.
Why not PMLs?
Despite their success in many applications, deriving a stable formulation of Perfectly Matched Layers (PML) for general coupled acoustic-elastic media on arbitrarily shaped domains using continuous Galerkin spectral-elements is an open research question.
That being said, implementing PMLs within Salvus is on the wish list, although not imminently planned.
Further reading
More information on the practical use of absorbing boundaries can be found on the following pages:
- the simple config interface in SalvusFlow,
- the low-level description in the SalvusCompute API,
- a tutorial using the Dirichlet condition and absorbing boundaries on different side sets.
References
Sommerfeld, A.: Die Greensche Funktion der Schwingungsgleichung. Jahresbericht der Deutschen Mathematiker-Vereinigung, 21(1), pp. 309-353, 1912.
Clayton, R. and Engquist, B.: Absorbing boundary conditions for acoustic and elastic wave equations: Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 67 (6), pp. 1529-1540, 1977. doi
Kosloff, R. and Kosloff, D.: Absorbing Boundaries for Wave Propagation Problems. Journal of Computational Physics 63(2), pp. 363-376, 1986. doi: 10.1016/0021-9991(86)90199-3
 Mondaic
Mondaic